Who Is Responsible for Secure Web Browsing? Everything About Certificate Authorities
In my previous article "How to Better Understand the Internet", we shortly mentioned the role of CAs (Certificate Authorities) and what they have to do with Digital Signatures.
In this post, I would like to a bit more about the different types of CA's and discuss further aspects, such as the following:
- Who Are CA's?
- Who Determines They Can Be Trusted?
- What Are the Different Types of CAs?
- When Do They Revoke Certificates?
Let's take a look.
Who Are These Certificate Authorities?
So as you probably know, Certificate Authorities issue Digital Certificates.
These certificates serve as proof that the website, individuals, or devices are legit and have the appropriate safety mechanisms implemented.
CAs play a crucial role in the safety of our network because, without them, you could never fully trust surfing the internet, without someone stealing your information.
They help protect against online threats, such as identity theft, phishing attacks, and more.
This is what a certificate looks like, and you can see the CA that issued the certificate:
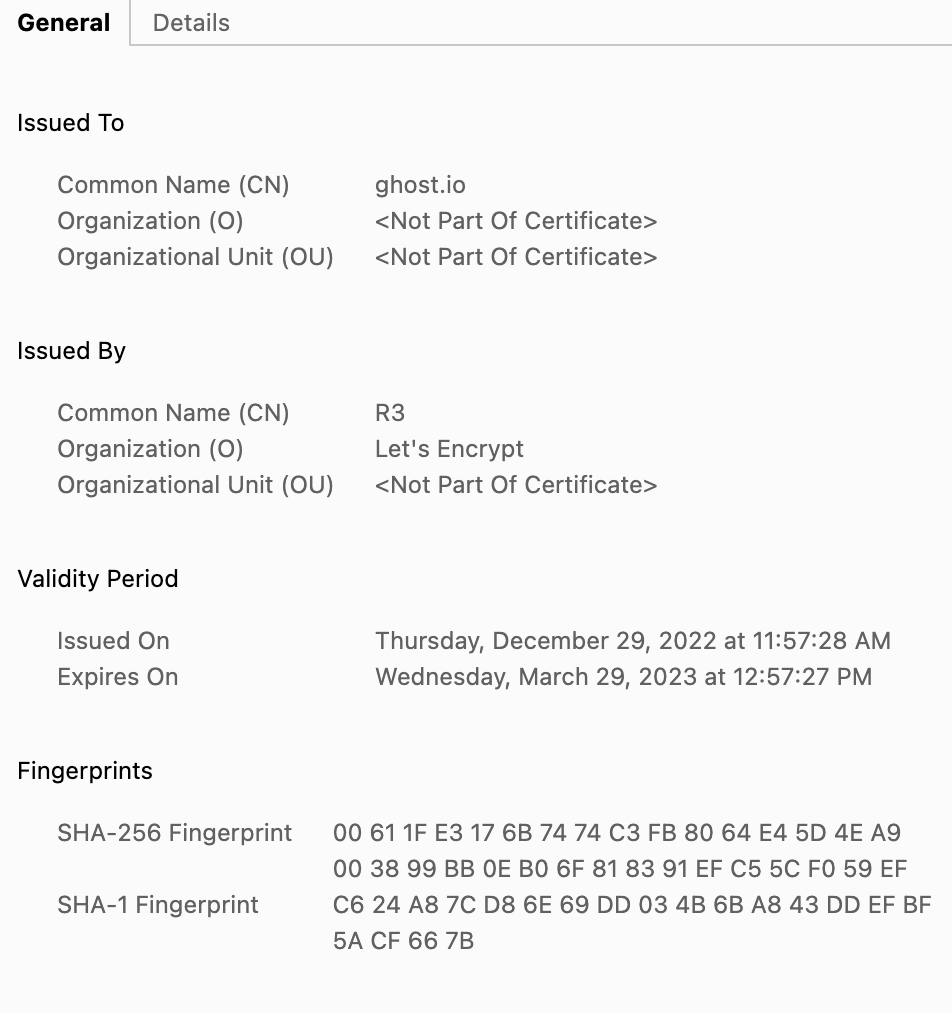
In this case, it's "Let's Encrypt".
Who Determines if CAs Can Be Trusted?
It is the different vendors of the operating system or browser.
They maintain a trusted list of CA providers.
It is determined who makes it on that list by checking what security measures the CA meets.
Do they have the minimum amount of security standards implemented? If yes, they make it on the trusted list.
Vendors usually perform audits on CAs.
These audits include the following areas:
- Proper Key Management
- Check for weaknesses in securities controls
- Review of policies and procedures
- Certificate issuance and management processes
- Pen testing/Compliance testing
- A report with a summary is issued
Besides auditing, there are other factors that come into play, such as:
- Reputation in the industry
- Track Record for Issuance of Certificates
- The ability for Incident Response
Once the vendors approve, the CAs can issue certificates.
What Are the Different Types of CAs?
In general, there are 5 types of Certificate Authorities.
In the most common hierarchies, you will find these 3 types:
- Root CA
The root is the highest level of CAs. It is fully trusted by the vendors of the OS.
- Issues certificates
- Signes Digital Certificates for Intermediary CAs
2. Intermediary CA
The intermediary CA is not trusted by the OS vendor. Therefore their issuance is only valid if signed by a Root CA.
They are responsible for the issuance of certificates for the Issuing CA.
3. Issuing CA
This is the authority that issues the certificates directly to the end entity, such as websites or individuals.
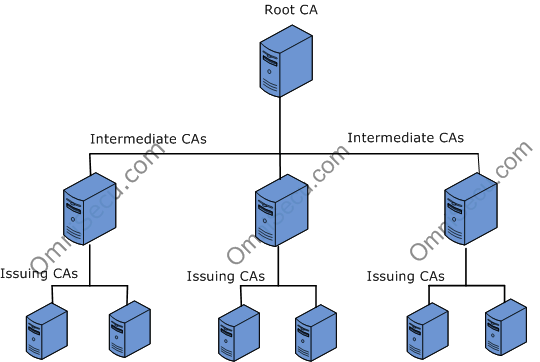
There exist other types of authorities such as:
4. Registration Authority (RA)
This is an intermediary between the entity requesting a certificate (web browser, individual) and the CA.
They are responsible for the identification of the entity requesting the certificates by:
- Doing background checks
- Verifying identification documents
After that, the request for issuing a certificate is forwarded to the CA.
5. Policy Authority (PA)
Establishes policies and procedures within the hierarchy.
So the PA manages who does the identity validation, who can revoke and renew certificates, and so on.
He defines the rules and roles.
When Are Certificates Revoked?
Certificates are revoked and out on the CRL (Certificate Revocation List) when:
- The private key is compromised
Should the private key be compromised or stolen, we do have a problem...
Since attackers could encrypt sensitive information, the CAs revoke the certificates to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Misuse and Policy Breach
When the certificate is used for purposes that it's not intended for and/or violates the policies, the CA immediately revokes the certificate.
3. Expiration
Expired Certificates are no longer in use and are therefore put on the list.
4. Mistake in Issuance
If there has been a mistake in the process
5. Request by the holder
If the certification holder wishes the certificate to be revoked, for specific reasons, he/she can do so.
6. Key Pair Update
If the key pair is updated, a new certificate will be created and the old one has to be revoked, so only the new version is valid.
Conclusion
So, that was an overview of the different CAs that are out there and who is responsible for what tasks.
I hope you could gain a deeper insight into the various responsibilities and the processes behind Digital Certificates.
Next time you're sitting in a meeting and someone mentions CAs, you'll know what they're talking about.
